There are many people suffering from diabetes, and many more who may suffer from it in the future due to their current lifestyle. However, another shocking truth is that there are people who have diabetes but are not aware of it. The biggest problem with diabetes is that it is often asymptomatic, which is why it is called the silent killer. The following article discusses terms like prediabetes, type 1 and type 2 diabetes, and most importantly, insulin resistance, and how to reverse diabetes while considering insulin resistance.
What is Prediabetes?
The expected value of a fasting sugar test should be between 70 mg/dL and 100 mg/dL (WHO – World Health Organization). A fasting sugar level between 100 and 125 mg/dL is called prediabetes, while a level above 125 mg/dL confirms type 2 diabetes.
| Fasting Sugar Level Value (mg/dL) | Condition |
| 70 – 100 | Normal |
| 100 – 125 | Prediabetic |
| >125 | Diabetic |
Prediabetes is a condition in which blood sugar levels are high but not high enough to fall under the category of type 2 diabetes. Prediabetes is neither a normal nor a diabetic condition; it is in between. The term prediabetes was created to inform people that they are on the borderline. If they do not change their lifestyle, they will likely become diabetic within the next 2 to 3 years.
What is the Basic Difference between Type 1 Diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes
One question that arises in people’s minds is how to differentiate between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. It’s a very valid question and one must be clear about it. Type 1 diabetes is generally diagnosed at a younger stage, i.e., in children, adolescents, and young adults. It could also be genetic in nature.
Type 1 diabetes occurs when no insulin or very low insulin is produced in the pancreas. This can be confirmed by undergoing a fasting insulin level test. The normal level of insulin in blood ranges from 2.5 to 25 µIU/ml. If the insulin level in the blood is below the normal range, it confirms type 1 diabetes. If the blood insulin level is above the normal range, it confirms type 2 diabetes. In other words, type 2 diabetes occurs due to high production of insulin in the body, while type 1 diabetes occurs due to low insulin production. More insulin causes insulin resistance, which eventually leads to type 2 diabetes.
How Severe is My Type 2 Diabetes?
Another question that comes to people’s minds is how to determine the severity of their type 2 diabetes. In other words, a person with type 2 diabetes wants to know the severity of their disease. The severity of the disease can be determined by measuring insulin resistance. Measuring insulin resistance is easy and requires the results of two blood tests: fasting insulin level and fasting blood sugar level.
Formula for Insulin Resistance

If the value of insulin resistance is between 0.5 and 1.49, there is no insulin resistance. If the value is between 1.5 and 2.5, there is moderate insulin resistance. If the insulin resistance value is above 2.5, there is severe insulin resistance.
What is Insulin Resistance?
Insulin resistance is linked to metabolic syndrome, which includes high blood glucose, high blood pressure, abdominal obesity, and high triglycerides. Together, these factors significantly increase the risk of other diseases such as heart attacks, stroke, and cancer. Because insulin resistance is associated with severe diseases, it is important to understand what it is and how to treat it.
Insulin is a natural hormone secreted by the pancreas. After eating, when nutrients are absorbed by the body, glucose molecules, the simplified carbohydrates flowing in the blood, enter the cells where they are further broken down to release energy. This energy is then utilized to perform various body functions.
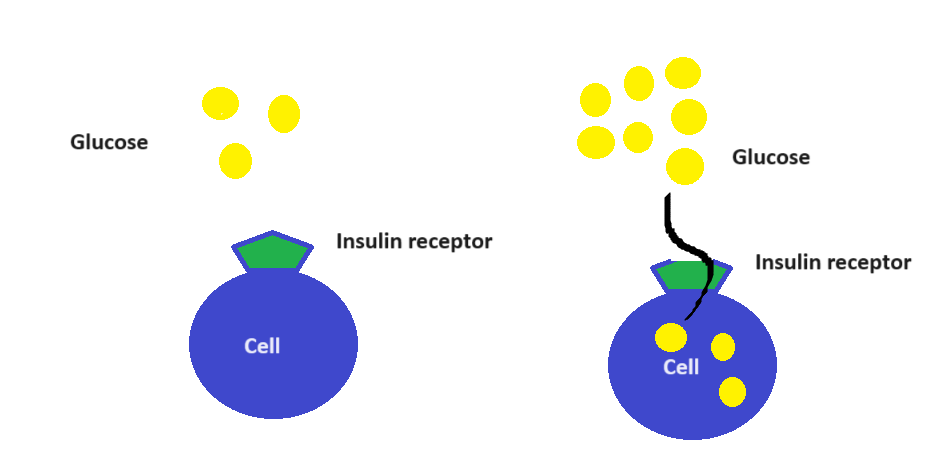
The question is, how does glucose enter the cells? Each cell, such as a liver cell, has a surface attached to an insulin receptor. When the glucose level rises after eating, it triggers the insulin receptor to allow glucose to enter the cell. In other words, the insulin receptor acts as a gatekeeper for the cell. When the level of glucose molecules in the blood rises after eating, the gatekeeper (insulin receptor) opens the door, and glucose molecules enter the cell. This process helps maintain the blood glucose level.
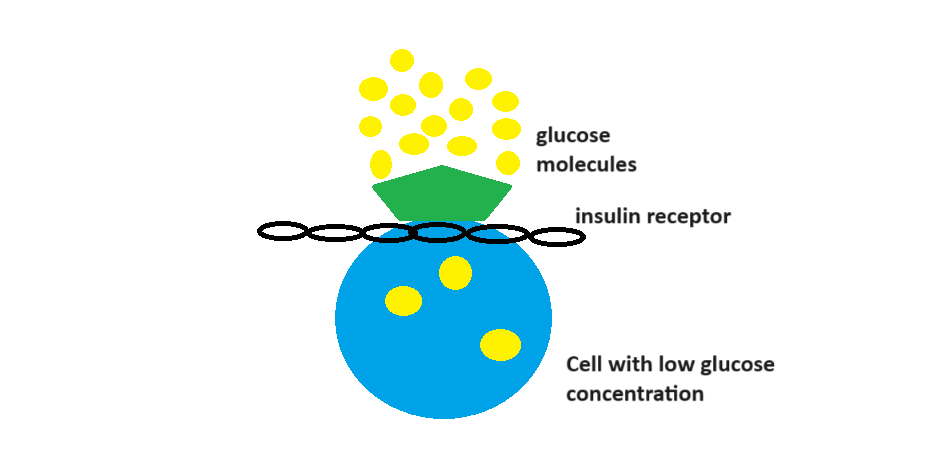
In cases of insulin resistance, even though there is enough insulin present in the blood, the number of glucose molecules remains high in the blood. In a normal situation, the glucose molecules should enter the cell, but this does not happen in cases of insulin resistance. Why is this so? There are two ways to think about it.
In cases of insulin resistance, even though there is enough insulin present in the blood, the number of glucose molecules remains high in the blood. In a normal situation, the glucose molecules should enter the cell, but this does not happen in cases of insulin resistance. Why is this so? There are two ways to think about it.
Firstly, something may be resisting the entry of glucose into the cell, which is why the cell does not have enough glucose molecules. If this logic were true, individuals with diabetes should appear skinny, but this is not the case. People with diabetes often have a big tummy, fatty liver, etc.
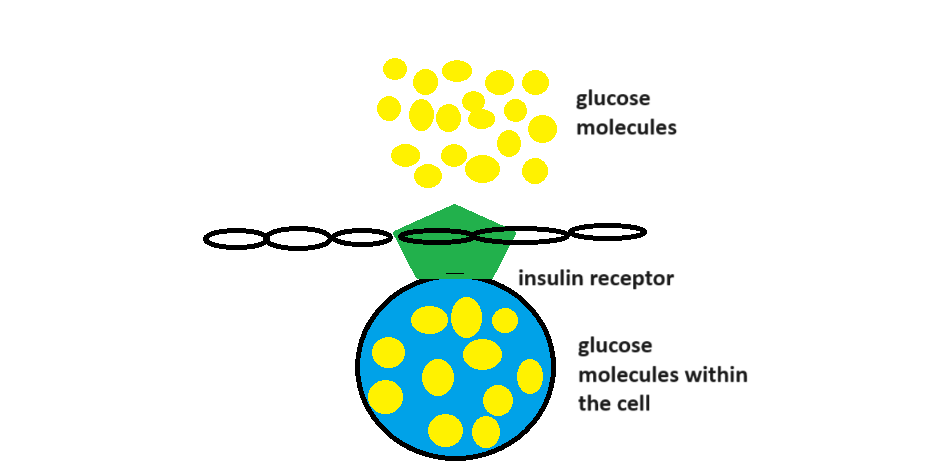
Another aspect of insulin resistance to consider is that if a cell already has enough glucose molecules, then no further glucose molecules can enter the cell. You might ask why cells already have many glucose molecules. This occurs over a long period of time when more and more glucose molecules accumulate inside the cell. Eventually, a point is reached where no further glucose molecules can enter the cell. As a result, the blood glucose level remains high. It can be predicted that a person with insulin resistance will have a fatty liver and obesity.
To reduce insulin resistance levels in the blood, several practices can be followed regularly. Fasting, a low-carbohydrate diet, and weight loss are the most common practices to reduce insulin resistance.
Diabetes Reversal Program
Insulin resistance is a reversible process and thus diabetes is also a reversal process. Under diabetes reversal program, one needs to follow certain rules of thumb:
- Restrict carbohydrate in diet
- Restrict glycemic index load in diet
Once the amount of sugar in the blood decreases, insulin use becomes less and thus insulin resistance starts reducing.
How will I Know that My Diabetes has been Reversed?
Before starting a diabetes reversal program, check your insulin resistance. Afterward, follow the diabetes reversal program and check your insulin resistance every three months. Once the insulin resistance level drops below 1.5, it indicates that diabetes has been reversed.
Many times, after starting a diabetes reversal program, blood sugar levels normalize within just a week. However, this cannot be considered diabetes reversal. Diabetes reversal can only be claimed when blood sugar levels are in the normal range and insulin resistance levels are at 1 or between 1 and 1.5.
Some people also wonder if they can compensate for higher carbohydrate and junk food intake by exercising more. It’s important to note that exercise is associated with burning calories, while insulin resistance is associated with blood sugar levels. In other words, exercise alone cannot reverse diabetes. Exercise is beneficial and can reduce blood sugar levels, but it cannot reverse diabetes. It is therefore important to control carbohydrate intake and consider the glycemic load in your diet.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q. What is fasting blood glucose test and what should be the normal value, prediabetic value and diabetic value?
A. Fasting blood glucose test is done after a gap of 8-10 hours from the last night meal. The blood sugar range should be between 70 mg/dL to 100 mg/dL. If the test range is between 100 and 125 mg/dL – it is considered as prediabetic and anything above 125 mg/dL confirms type 2 diabetes.
Q. What do you mean by random sugar test?
A. A random sugar test can be done anytime in a day irrespective of what time you had your last meal. A random sugar level of above 200 mg/dL confirms diabetes.
Q. What is glucose tolerance test?
A. This is also called as PP (Post-prandial) test where the first glucose test is taken after 8-10 hours of fasting. And then sugary liquid is given to drink immediately. After a wait of 2 hours from taking the sugary drink, another glucose test is done. A blood sugar level if less than 40 mg/dL is considered normal. A reading between 140 and 199 mg/dL is considered prediabetic and above 200 mg/dL is considered as diabetic condition.
Q. What is the normal level of insulin resistance?
A. Insulin resistance between 0.5 and 1.49 is considered normal; between 1.5 and 2.5 is considered as moderate insulin resistance and above 2.5 is considered as severe insulin resistance.