Stroke is one of the leading health issues in the United States. Approximately 800,000 strokes occur every year in the United States. It occurs when there is an unexpected interruption of blood flow to the brain. There are primarily, two types of strokes: ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. The following article covers all aspects of stroke, including its causes, symptoms, risk factors, prevention, and treatment. Read the following article to understand the disease better
Understanding Stroke
A stroke is not an accident. The powerful human brain is the basis for everything we do including our thoughts, words, emotions, and interactions with others. The brain is also affected by haemorrhage.
All strokes have underlying causes. They result from a sudden disruption of blood flow to the brain. Stroke is characterized by two main types:
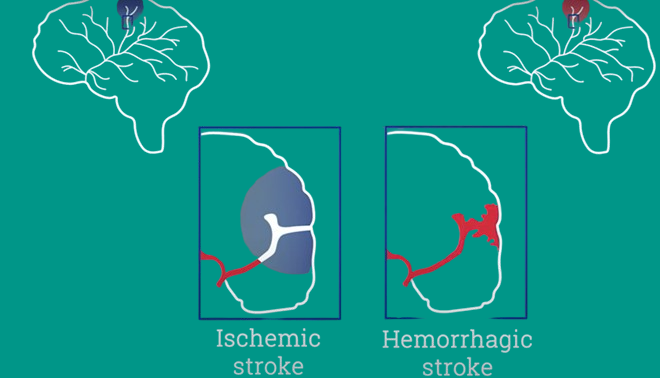
Ischemic Stroke
In this type of stroke, a blocked artery can cut-off blood flow to an area of the brain. This is known as an ischemic stroke, the most common type, accounting for 85 percent of all strokes.
Hemorrhagic Stroke
It occurs when a blood vessel can leak or burst. As a result, blood fills inside the brain tissue or surrounding the brain.
The human brain is highly demanding and requires a large blood supply. When blood flow is disrupted, for instance, by a tiny blood clot traveling to a brain vessel and occluding it, brain cells begin to die. This can happen within minutes of the disruption, which is why it is an emergency. Patients experiencing any type of stroke, no matter how minor, should seek urgent medical evaluation from health professionals to prevent damage, disability, or even death.
Stroke Warning Signs
It is very crucial to recognize stroke signs and quickly reach the hospital. This can help save your precious life. There are five warning signs of stroke:
- An Unexpected numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, particularly on one side of the body.
- Abrupt confusion, difficulty speaking, or trouble understanding what someone is saying to you.
- An Unexpected difficulty seeing in one or both eyes.
- Abrupt difficulty walking, dizziness, or loss of balance.
- An unexpected, intense headache with no apparent cause.
Strokes in Women: Are they different from Men?
The answer to this question could be both yes and no. No, because a stroke primarily depends on which part of the brain is affected by either ischemia or bleeding. Thus, whether it involves difficulty speaking or paralysis, men and women often experience strokes in a very similar manner. However, women sometimes experience stroke symptoms differently, with milder symptoms that might be accompanied by a headache or a general feeling of unwellness. This difference is what sets stroke in men and women apart. Additionally, other factors differentiate it between men and women:
- Women are often stoic
- Women are primary caretakers for others
- Women underestimate and underreport their symptoms
Strokes in Young Adults
It feels fundamentally unfair to have a stroke when you are young and otherwise healthy. Stroke is often viewed as an illness associated with old age, and the majority of strokes occur in older adults. However, it’s not just a matter of when, but why the same risk factors commonly seen in older individuals are also present in those in their 20s, 30s, and 40s. Some of the most common risk factors for stroke in young adults are the usual suspects, such as:
- High blood pressure (HBP)
- Diabetes
- High cholesterol
- Smoking
- Drug use
- Infections (including COVID)
- Exposure to OTC (Over the Counter) health supplements
- Energy drinks
There are of course rare conditions that affect the risk of strokes in younger individuals that they have no control over.
Stroke Risk Factors
Stroke is just the tip of the iceberg. It isn’t a disease on its own rather, it’s a sign of an underlying issue within the body. Over three-quarters of strokes have a clear underlying cause, which can be directly linked to blood vessel damage in the brain. These well-known conditions are called risk factors because they are directly connected to the risk of stroke.
The most common risk factors are conditions that are well-known and highly treatable. These include:
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- High cholesterol
- Smoking
- Excessive alcohol use
- Stress
All of the above-mentioned risk factors can be treated effectively, preventing the majority of strokes occurring in the United States and worldwide. Age is another risk factor for stroke, with the risk increasing proportionally for individuals over the age of 55 with each passing decade. Additionally, strokes are more frequent in individuals of African-American descent as well as those of Hispanic ethnicity.
For some individuals, the risk of stroke increases because their parents had such a condition and were referred to that condition as familial even though stroke is not a genetic disease. No matter what risk factors are there, one thing to remember is that you are not a victim of stroke. It is a leading cause of disability and death in the United States and globally which is of course a great concern to the medical community and should be concerning to the public. There is also a reason for optimism. Health professionals often say, “Stroke is preventable, treatable, and beatable.” The goal of many healthcare professionals worldwide is to ensure that stroke-related disability and death are a thing of the past. The fact is that health professionals can identify most of the underlying causes of strokes which gives them great optimism. If they can diagnose the reasons, they can effectively treat patients.
Despite all efforts, a stroke will happen in the future. The best thing one can do is to educate yourself and your loved ones about stroke. Know your risk of stroke and take every measure to prevent it, but know the signs and symptoms of stroke and act fast to maximize the chance of stroke recovery.
What Common Mistakes People do?
The most common mistake people make is waiting for the symptoms to go away. Avoid waiting for the symptoms to resolve on their own. There is a saying in neurology: ‘Time is brain.’ Each minute that passes leads to the death of brain cells, resulting in irreversible damage. Another common mistake is taking an aspirin, as one might do during a heart attack. In the case of a stroke, this is wrong and potentially dangerous, especially in a hemorrhagic stroke. Instead, go to the hospital immediately so that health professionals can perform early diagnostics, such as a brain scan or a CT scan (Computed Tomography). Additionally, they can administer powerful medications.
Another type of therapy that health professionals can offer is called Thrombectomy. It is a surgical intervention similar to cardiac catheterization except that the catheter goes all the way into the brain vessels to remove the clot directly. This is a special procedure that very highly trained doctors perform at stroke centres.
Stroke Prevention
Preventing stroke is easier than you think. After decades of research, the American Heart Association and the American Stroke Association developed a straightforward approach known as “Life’s Simple Seven”. This is a collection of guidelines they recommend to prevent heart disease and stroke:
- Quit smoking
- Manage blood pressure
- Eat healthy
- Control cholesterol
- Get physically active
- Reduce blood sugar
- Lose weight
All these measures have scientific underpinning and specific goals. For example, health professionals ask patients to exercise a minimum of 150 minutes a week. Moderate exercise like walking will do and it is better if it is done every day. Mindfulness also could be a measure of getting a handle on stress. There are also specific goals for blood pressure, blood sugar, and cholesterol levels. However, it is always better to consult your doctor to understand your risk of stroke.
Stroke Treatment and Recovery
Once the stroke is diagnosed and managed in the very early stages, your doctor will formulate a personalized plan for your prevention, treatment, and recovery. You will also require physical, occupational, or speech therapy to help you recover after a stroke. Since every individual recovers at a different rate after a stroke, you need to stay in touch with your primary healthcare doctor and with your neurologist to help you in your recovery.
Conclusion
Stroke is a serious health issue in the U.S., with about 800,000 cases each year. This article covers key aspects of stroke, such as its causes, symptoms, types, and risk factors. Recognizing stroke signs early and acting fast can save lives. Preventative measures and prompt treatment are vital for reducing the impact of stroke and improving recovery outcomes.